Overview
Digital planning and guided surgery have revolutionized dental implant procedures, offering improved precision and predictability. The integration of affordable 3D printing technology has democratized access to these advanced techniques, allowing more dental practices to deliver high-quality implant treatments. While theoretical cases often present ideal conditions, real-world implantology requires practitioners to navigate unexpected complications with adaptable solutions and comprehensive understanding of both digital and conventional techniques. The following webinar emphasize the importance of combining technical expertise with practical problem-solving skills, ensuring successful outcomes in guided implant surgery.
Essential Principles
Modern guided surgery represents a significant evolution in implant dentistry, combining advanced surgical kits with sophisticated digital planning tools. The Alpha-Bio Tec. kit exemplifies this progression with its multi-purpose functionality, ergonomic design, and built-in depth control.
Key features include:
- Key-less Guided system enabling one-handed operation
- Guided Surgical System compatible for multiple implant connection types
- Enhanced precision through built-in depth control mechanisms
- Ergonomic design optimized for surgical efficiency
However, practitioners must be prepared to address common challenges such as alignment issues, space limitations, and guide adaptation problems that frequently arise in clinical settings.
Clinical Protocol
The surgical process demands both a systematic approach and the flexibility to adapt to individual case requirements. Essential elements include:
Preparation Phase:
- Comprehensive site preparation using tissue punch tools and crestal drills
- Clinical Bone assessment prior to final drilling
- Strategic planning of implant positioning and angulation
Drilling Sequence:
- Initial use of shorter drills (8mm) before progressing to longer sizes
- Modified drilling speeds (1500-2000 RPM) to prevent deviation
- Progressive diameter increase for optimal stability
- Careful monitoring of bone integrity throughout the sequence
Implant Placement:
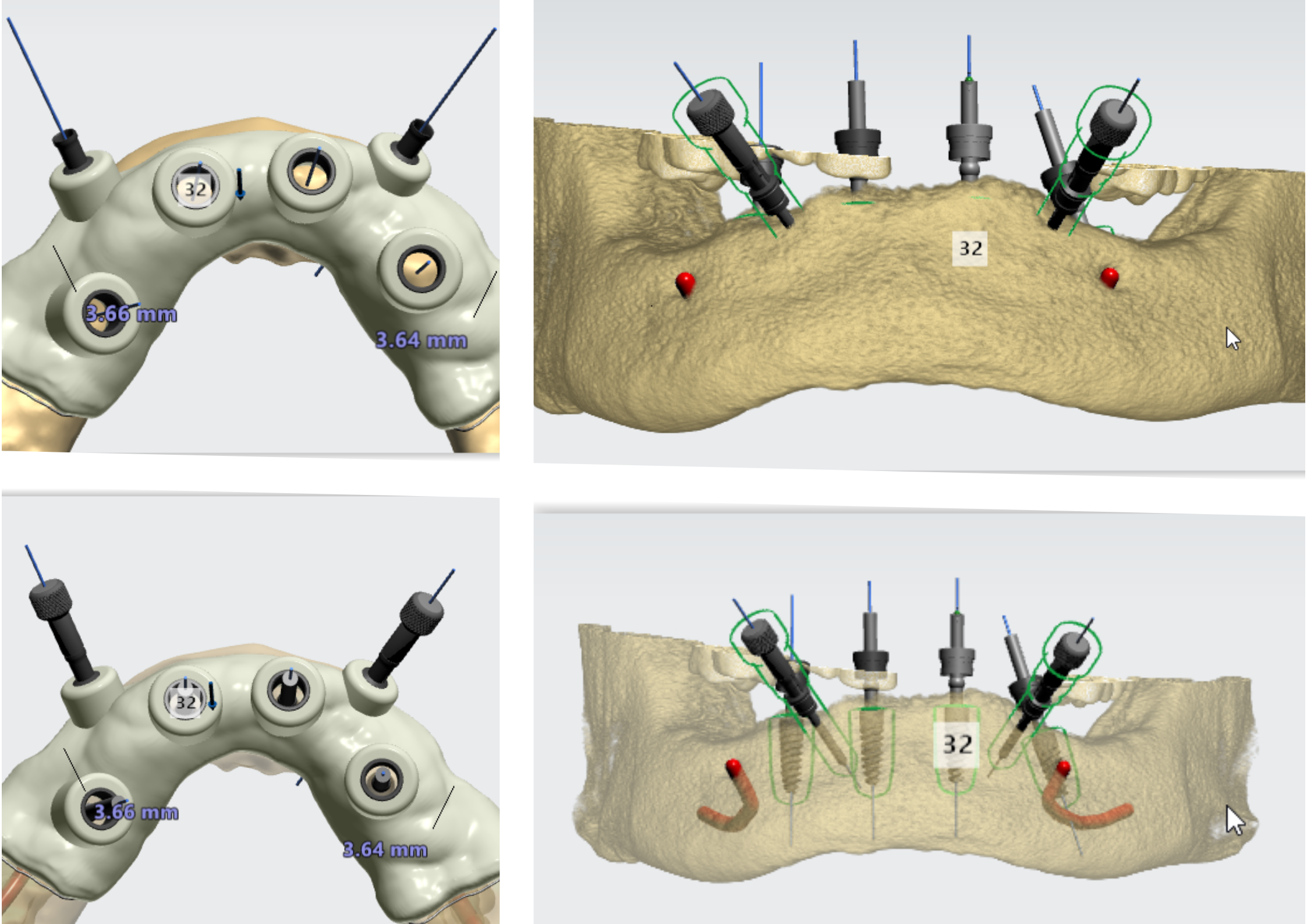
- Strategic use of specialized sleeves for different implant sizes
- Implementation of cross-pattern distribution for multiple implants
- Verification of parallelism using long screws
- Adjustment of offset parameters for optimal implant depth
Clinical Challenges and Solutions
Real-world implant procedures often present complex challenges requiring specific solutions:
1. Alignment Issues
- Problem: Automatic STL alignment tools can misplace models
- Solution: Implementation of point-based manual alignment techniques
- Benefits: Enhanced precision and control over final positioning
2. Limited Space Management
- Challenge: Narrow spaces in lateral incisors and lower anteriors
- Approach: Adjustment of offset parameters and drill depth compensation
- Outcome: Improved access while maintaining precise positioning
3. Free-End Cases
- Issue: Limited posterior support affecting guide stability Solutions:
- Integration of mucosal markers (glass beads or adhesive markers)
- Utilization of digital overlays for improved bone structure alignment
- Enhanced guide adaptation techniques
4. Post-Extraction Implants
- Complications: Existing tooth structure interfering with guide placement Resolution:
- Performance of virtual extractions in planning software
- Strategic guide modifications to avoid interference
- Careful consideration of post-extraction site morphology
5. Soft Quality Bone Management
- Challenge: Accurate assessment of bone density in guided systems Approach:
- Implementation of manual bone assessment protocols
- Modified drilling sequences with progressive expansion
- Careful management of primary stability
3D Printing Applications
Modern guided surgery increasingly relies on 3D printing technology, which has become both more accessible and more precise:
1. Technology Selection:
- Resin-based 3D printers recommended for dental applications
- Trusted and cost-effective brands in the market include Anycubic, Elegoo, and Phrozen
- Affordable entry-level printers priced at $500-$600 offer professional-grade precision
2. Technical Considerations:
- Critical importance of proper resin selection for durability
- Sterilization compatibility requirements
- Customized setting for various implant systems
3. Implementation Benefits:
- Significant cost reduction compared to traditional methods
- Maintained precision comparable to expensive systems
- Increased accessibility for dental practices
- Enhanced ability to create custom solutions
Clinical Applications
Successful implementation of guided surgery requires attention to numerous technical details:
- Precise calibration of 3D printing parameters
- Regular verification of guide accuracy
- Strategic use of fixation methods
- Integration with digital workflow systems
- Ongoing monitoring and adjustment of protocols
About the Speaker
Dr. Pablo Matamala, a specialist in bucomaxillofacial implantology from the University of Chile, brings extensive experience in guided surgery, digital planning, and 3D printing for dental implants. His expertise helps practitioners navigate the complexities of modern implant procedures while implementing practical solutions to real-world challenges.
Click here to watch te webinar on demand.

Related Blogs
Education | Clinical Case

Education at the Heart of Alpha-Bio Tec. - Our 2026 Vision
Education | Webinar on-demand

.jpeg)